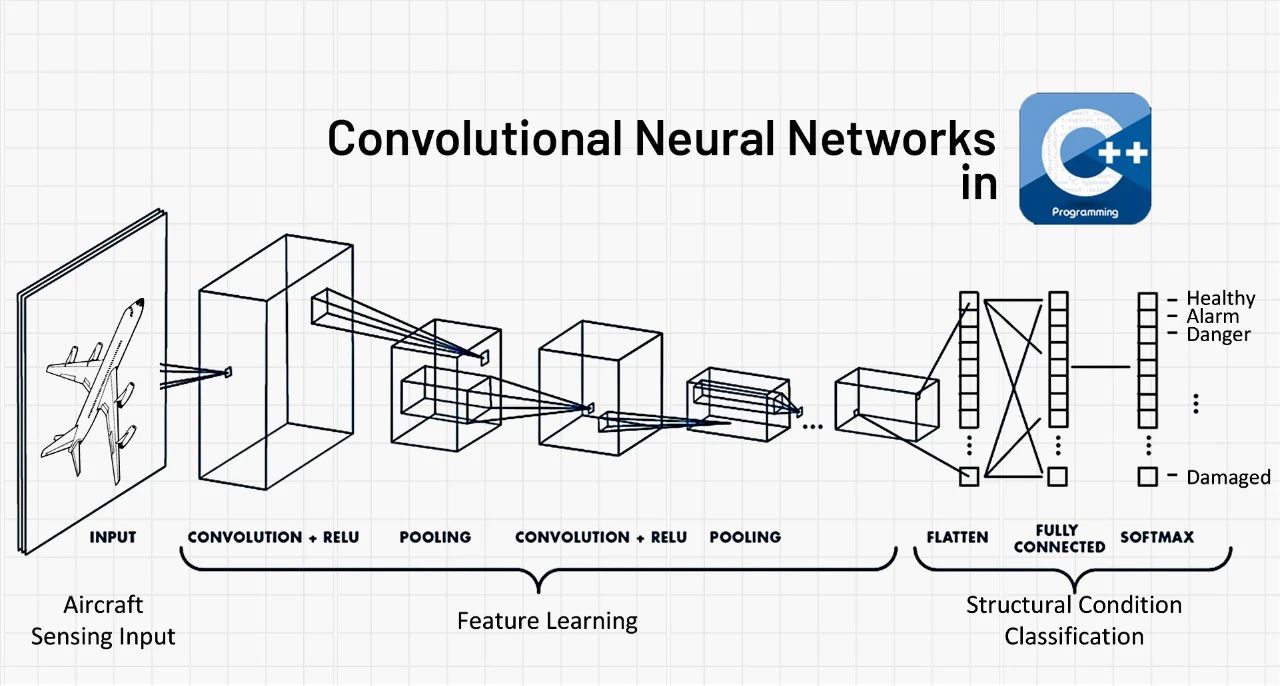
有很多卷积神经网络文章解释了 CNN 是什么以及它的用途是什么,而本文将用 C++ 编写一个 CNN 和一个名为 mlpack 的库来对MNIST数据集进行分类。
你们可能会问为什么 C++ 在 Python 中很容易使用大量库,你们现在可能已经看到一些特斯拉汽车,这些类型的系统需要从它们的环境中进行实时推理,而 Python 非常适合原型设计,但不提供实时当使用它部署如此庞大的模型时会更新。
一、mlpack的含义
它是一个用 C++ 编写的机器学习库,它利用其他一些底层库来提供快速且可扩展的尖端机器学习和深度学习方法。
二、MINST数据集
我们要使用的数据包含在一个 CSV 文件中,由 0 到 9 的数字图像组成,其中列包含标签,行包含特征,但是当我们要将数据加载到矩阵中时,数据将被转置,并且提到哪个特征的标签也将被加载,所以我们需要注意这一点。
#include <mlpack/core.hpp> #include <mlpack/core/data/split_data.hpp> #include <mlpack/methods/ann/layer/layer.hpp> #include <mlpack/methods/ann/ffn.hpp> #include <ensmallen.hpp> /* The numerical optimization library that mlpack uses */ using namespace mlpack; using namespace mlpack::ann; // Namespace for the armadillo library(linear algebra library). using namespace arma; using namespace std; // Namespace for ensmallen. using namespace ens;
然后我们将声明一个辅助函数将模型输出转换为行矩阵,以匹配我们加载的行矩阵形式的标签。
arma::Row<size_t> getLabels(arma::mat predOut)
{
arma::Row<size_t> predLabels(predOut.n_cols);
for(arma::uword i = 0; i < predOut.n_cols; ++i)
{
predLabels(i) = predOut.col(i).index_mat() + 1;
}
return predLabels;
}在这一部分下面,代码将出现在main函数中,但它的编写并不是为了让代码易于解释。现在我们将声明一些我们需要的明显训练参数,将解释那些突出的参数。
constexpr double RATIO = 0.1; // ratio to divide the data in train and val set.
constexpr int MAX_ITERATIONS = 0; // set to zero to allow infinite iterations.
constexpr double STEP_SIZE = 1.2e-3;// step size for Adam optimizer.
constexpr int BATCH_SIZE = 50;
constexpr size_t EPOCH = 2;
mat tempDataset;
data::Load("train.csv", tempDataset, true);
mat tempTest;
data::Load("test.csv", test, true);参数 MAX_ITERATIONS 设置为 0,因为这允许我们在一个 epoch 中无限迭代,以便在训练阶段后期使用提前停止。作为旁注,当此参数未设置为 0 时,也可以使用提前停止。
让我们处理和删除描述每一行中包含的内容的列,如我在数据部分所述,并为训练、验证和测试集的标签和特征创建一个单独的矩阵。
mat dataset = tempDataset.submat(0, 1, tempDataset.n_rows - 1, tempDataset.n_cols - 1); mat test = tempTest.submat(0, 1, tempTest.n_rows - 1, tempTest.n_cols - 1); mat train, valid; data::Split(dataset, train, valid, RATIO); const mat trainX = train.submat(1, 0, train.n_rows - 1, train.n_cols - 1); const mat validX = valid.submat(1, 0, valid.n_rows - 1, valid.n_cols - 1); const mat testX = test.submat(1, 0, test.n_rows - 1, test.n_cols - 1); const mat trainY = train.row(0) + 1; const mat validY = valid.row(0) + 1; const mat testY = test.row(0) + 1;
我们将使用负对数似然损失,在 mlpack 库中,它的标签从 1 而不是 0 开始,因此我们在标签中添加了 1。
三、卷积框架
现在让我们看一下我们将要定义的简单卷积架构。
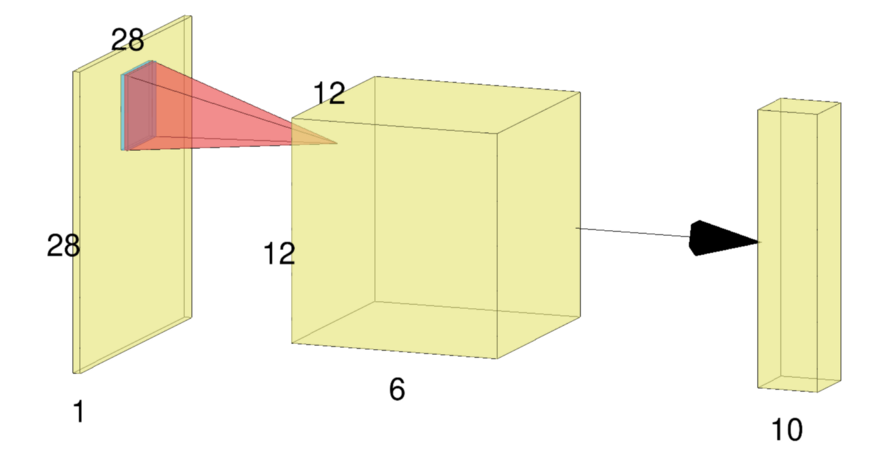
FFN<NegativeLogLikelihood<>, RandomInitialization> model; model.Add<Convolution<>>(1, // Number of input activation maps. 6, // Number of output activation maps. 5, // Filter width. 5, // Filter height. 1, // Stride along width. 1, // Stride along height. 0, // Padding width. 0, // Padding height. 28, // Input width. 28 // Input height. ); model.Add<ReLULayer<>>(); model.Add<MaxPooling<>>(2, // Width of field. 2, // Height of field. 2, // Stride along width. 2, // Stride along height. true); model.Add<Convolution<>>(6, // Number of input activation maps. 16, // Number of output activation maps. 5, // Filter width. 5, // Filter height. 1, // Stride along width. 1, // Stride along height. 0, // Padding width. 0, // Padding height. 12, // Input width. 12 // Input height. ); model.Add<ReLULayer<>>(); model.Add<MaxPooling<>>(2, 2, 2, 2, true); model.Add<Linear<>>(16 * 4 * 4, 10); model.Add<LogSoftMax<>>();
其他细节的展示:
ens::Adam optimizer(
STEP_SIZE, // Step size of the optimizer.
BATCH_SIZE, // Batch size. Number of data points that are used in each iteration.
0.9, // Exponential decay rate for the first moment estimates.
0.999, // Exponential decay rate for the weighted infinity norm estimates.
1e-8, // Value used to initialise the mean squared gradient parameter.
MAX_ITERATIONS, // Max number of iterations.
1e-8, // Tolerance.
true);
model.Train(trainX,
trainY,
optimizer,
ens::PrintLoss(),
ens::ProgressBar(),
ens::EarlyStopAtMinLoss(EPOCH),
ens::EarlyStopAtMinLoss(
[&](const arma::mat& /* param */)
{
double validationLoss = model.Evaluate(validX, validY);
std::cout << "Validation loss: " << validationLoss
<< "." << std::endl;
return validationLoss;
}));正如你们可以看到在验证准确性上使用 EarlyStopAtMinLoss,这就是将参数 MAX_ITERATIONS 设置为 0 以让我们定义无限迭代的原因。
mat predOut; model.Predict(trainX, predOut); arma::Row<size_t> predLabels = getLabels(predOut); double trainAccuracy = arma::accu(predLabels == trainY) / ( double )trainY.n_elem * 100; model.Predict(validX, predOut); predLabels = getLabels(predOut); double validAccuracy = arma::accu(predLabels == validY) / ( double )validY.n_elem * 100; std::cout << "Accuracy: train = " << trainAccuracy << "%,"<< "\t valid = " << validAccuracy << "%" << std::endl; mat testPredOut; model.Predict(testX,testPredOut); arma::Row<size_t> testPred = getLabels(testPredOut) double testAccuracy = arma::accu(testPredOut == testY) /( double )trainY.n_elem * 100; std::cout<<"Test Accuracy = "<< testAccuracy;
本文代码链接:https://github.com/Aakash-kaushik
本文转自:小白学视觉,转载此文目的在于传递更多信息,版权归原作者所有。如不支持转载,请联系小编demi@eetrend.com删除。