本文转自CSDN,作者:mingo_敏
损失函数通过torch.nn包实现
基本用法
criterion = LossCriterion() #构造函数有自己的参数 loss = criterion(x, y) #调用标准时也有参数
19种损失函数
1. L1范数损失 L1Loss
计算 output 和 target 之差的绝对值。
torch.nn.L1Loss(reduction='mean')
参数:
reduction-三个值,none: 不使用约简;mean:返回loss和的平均值;sum:返回loss的和。默认:mean。
2. 均方误差损失 MSELoss
计算 output 和 target 之差的均方差。
torch.nn.MSELoss(reduction='mean')
参数:
reduction-三个值,none: 不使用约简;mean:返回loss和的平均值;sum:返回loss的和。默认:mean。
3. 交叉熵损失 CrossEntropyLoss
当训练有 C 个类别的分类问题时很有效. 可选参数 weight 必须是一个1维 Tensor, 权重将被分配给各个类别. 对于不平衡的训练集非常有效。
在多分类任务中,经常采用 softmax 激活函数+交叉熵损失函数,因为交叉熵描述了两个概率分布的差异,然而神经网络输出的是向量,并不是概率分布的形式。所以需要 softmax激活函数将一个向量进行“归一化”成概率分布的形式,再采用交叉熵损失函数计算 loss。

torch.nn.CrossEntropyLoss(weight=None,ignore_index=-100, reduction='mean')
参数:
weight (Tensor, optional) – 自定义的每个类别的权重. 必须是一个长度为 C 的 Tensor
ignore_index (int, optional) – 设置一个目标值, 该目标值会被忽略, 从而不会影响到 输入的梯度。
reduction-三个值,none: 不使用约简;mean:返回loss和的平均值;sum:返回loss的和。默认:mean。
4. KL 散度损失 KLDivLoss
计算 input 和 target 之间的 KL 散度。KL 散度可用于衡量不同的连续分布之间的距离, 在连续的输出分布的空间上(离散采样)上进行直接回归时 很有效.
torch.nn.KLDivLoss(reduction='mean')
参数:
reduction-三个值,none: 不使用约简;mean:返回loss和的平均值;sum:返回loss的和。默认:mean。
5. 二进制交叉熵损失 BCELoss
二分类任务时的交叉熵计算函数。用于测量重构的误差, 例如自动编码机. 注意目标的值 t[i] 的范围为0到1之间.
torch.nn.BCELoss(weight=None, reduction='mean')
参数:
weight (Tensor, optional) – 自定义的每个 batch 元素的 loss 的权重. 必须是一个长度为 “nbatch” 的 的 Tensor
6. BCEWithLogitsLoss
BCEWithLogitsLoss损失函数把 Sigmoid 层集成到了 BCELoss 类中。该版比用一个简单的 Sigmoid 层和 BCELoss 在数值上更稳定,因为把这两个操作合并为一个层之后, 可以利用 log-sum-exp 的 技巧来实现数值稳定。
torch.nn.BCEWithLogitsLoss(weight=None, reduction='mean', pos_weight=None)
参数:
weight (Tensor, optional) – 自定义的每个 batch 元素的 loss 的权重. 必须是一个长度 为 “nbatch” 的 Tensor
7. MarginRankingLoss
torch.nn.MarginRankingLoss(margin=0.0, reduction='mean')
对于 mini-batch(小批量) 中每个实例的损失函数如下:
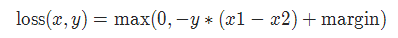
参数:
margin:默认值0
8. HingeEmbeddingLoss
torch.nn.HingeEmbeddingLoss(margin=1.0, reduction='mean')
对于 mini-batch(小批量) 中每个实例的损失函数如下:
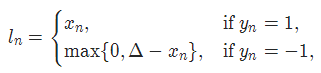
参数:
margin:默认值1
9. 多标签分类损失 MultiLabelMarginLoss
torch.nn.MultiLabelMarginLoss(reduction='mean')
对于mini-batch(小批量) 中的每个样本按如下公式计算损失:
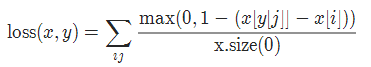
10 平滑版L1损失 SmoothL1Loss
也被称为 Huber 损失函数。
torch.nn.SmoothL1Loss(reduction='mean')

其中
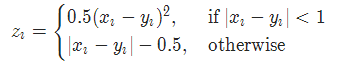
11. 2分类的logistic损失 SoftMarginLoss
torch.nn.SoftMarginLoss(reduction='mean')
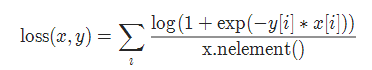
12. 多标签 one-versus-all 损失 MultiLabelSoftMarginLoss
torch.nn.MultiLabelSoftMarginLoss(weight=None, reduction='mean')
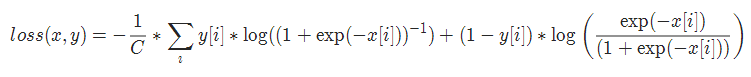
13. cosine 损失 CosineEmbeddingLoss
torch.nn.CosineEmbeddingLoss(margin=0.0, reduction='mean')
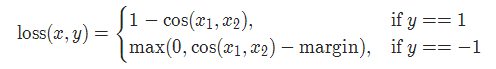
参数:
margin:默认值0
14. 多类别分类的hinge损失 MultiMarginLoss
torch.nn.MultiMarginLoss(p=1, margin=1.0, weight=None, reduction='mean')
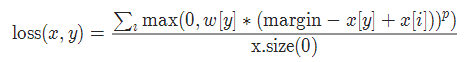
参数:
p=1或者2 默认值:1
margin:默认值1
15. 三元组损失 TripletMarginLoss
和孪生网络相似,具体例子:给一个A,然后再给B、C,看看B、C谁和A更像。
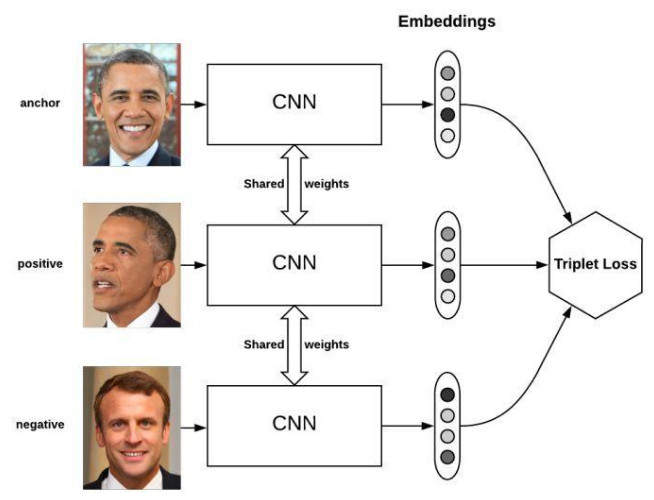
torch.nn.TripletMarginLoss(margin=1.0, p=2.0, eps=1e-06, swap=False, reduction='mean')
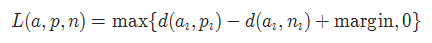
其中:
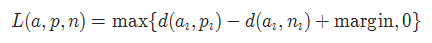
16. 连接时序分类损失 CTCLoss
CTC连接时序分类损失,可以对没有对齐的数据进行自动对齐,主要用在没有事先对齐的序列化数据训练上。比如语音识别、ocr识别等等。
torch.nn.CTCLoss(blank=0, reduction='mean')
参数:
reduction-三个值,none: 不使用约简;mean:返回loss和的平均值;sum:返回loss的和。默认:mean。
17. 负对数似然损失 NLLLoss
负对数似然损失. 用于训练 C 个类别的分类问题.
torch.nn.NLLLoss(weight=None, ignore_index=-100, reduction='mean')
参数:
weight (Tensor, optional) – 自定义的每个类别的权重. 必须是一个长度为 C 的 Tensor
ignore_index (int, optional) – 设置一个目标值, 该目标值会被忽略, 从而不会影响到 输入的梯度.
18. NLLLoss2d
对于图片输入的负对数似然损失. 它计算每个像素的负对数似然损失.
torch.nn.NLLLoss2d(weight=None, ignore_index=-100, reduction='mean')
参数:
weight (Tensor, optional) – 自定义的每个类别的权重. 必须是一个长度为 C 的 Tensor
reduction-三个值,none: 不使用约简;mean:返回loss和的平均值;sum:返回loss的和。默认:mean。
19. PoissonNLLLoss
目标值为泊松分布的负对数似然损失
torch.nn.PoissonNLLLoss(log_input=True, full=False, eps=1e-08, reduction='mean')
参数:
log_input (bool, optional) – 如果设置为 True , loss 将会按照公 式 exp(input) - target * input 来计算, 如果设置为 False , loss 将会按照 input - target * log(input+eps) 计算.
full (bool, optional) – 是否计算全部的 loss, i. e. 加上 Stirling 近似项 target * log(target) - target + 0.5 * log(2 * pi * target).
eps (float, optional) – 默认值: 1e-8
参考资料:
pytorch loss function 总结
http://www.voidcn.com/article/p-rtzqgqkz-bpg.html
本文转自CSDN,作者:mingo_敏,转载此文目的在于传递更多信息,版权归原作者所有。
原文链接:https://blog.csdn.net/shanglianlm/article/details/85019768






